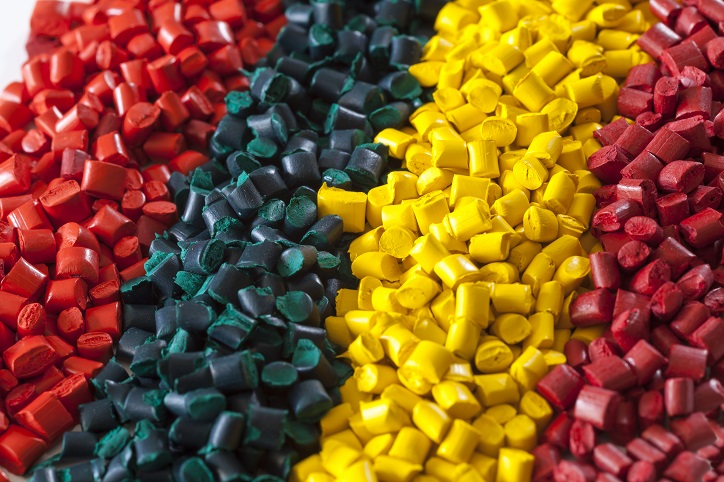
Talc is commonly used as part of masterbatches, which is a concentrated additive comprising high-concentrated pigments and other functional additions diffused in a carrying agent (normally a polymer). Using talc in masterbatches involves a range of advantages:
1. Improved dispersion: talc serves as a carrier of functional additions and pigments facilitating their uniform distribution in the polymer matrix. This contributes to better dispersion and enables even distribution of color and functional properties across the composite.
2. Increased durability: as a filler, talc provides additional mechanical strength of masterbatches, which may be relevant for various applications, especially for manufacturing plastic products.
4. Lower density: adding talc to masterbatches allows reducing material’s density, which is particularly useful when there is a need to decrease the weight of the finished product.
5. Improved thermal resistance: talc increases thermal resistance of masterbatches, which allows expanding the scope of material’s use at elevated temperatures.
6. Longer service life: Owing to their improved mechanical properties, masterbatches comprising talc may preserve their properties in the longer term and have better resistance to environmental impacts.
Importantly, using talc in masterbatches should be carefully considered, and talc powder size characteristics must be optimized in line with the specific project requirements. The correct selection of components and optimized masterbatch manufacturing process are essential aspects to achieve the desired properties and quality of the finished product.